
Security experts from Kaspersky have warned about a series of attacks targeted at distributors of equipment and software for industrial enterprises globally to steal Windows credentials. It is found that attackers are using phishing scams and steganography methods to hide malware on legitimate image and file resources.
In its report, Kaspersky stated that it identified a series of targeted attacks on organizations located in Japan, Italy, Germany, and the U.K. from May 2020. Hackers used malicious Microsoft Office documents, PowerShell scripts, and other sophisticated techniques like steganography to escape detection. While the ultimate goal of the attackers is unknown, Kaspersky stated that hackers used Mimikatz utility to steal the authentication data of Windows accounts stored on a compromised system.
“Phishing emails, used as the initial attack vector, were tailored and customized under the specific language for each specific victim. The malware used in this attack performed destructive activity only if the operating system had a localization that matched the language used in the phishing email,” researchers said.
Steganography
Steganography is an ancient practice of hiding secret content and text messages inside non-suspicious messages. Cybercriminals use this technique to hide malicious code within the image/audio/text file that is mainly employed by exploiting kits to hide their malvertising traffic. If the victim clicks the document, the script will execute and downloads the image hosted online which contains the malicious code.
Attack Chain
The phishing emails from attackers contain an urgent request to open the malicious attachment. Hackers send an Excel spreadsheet with a malicious macro or a malicious image (using Steganography technique) and ask users to enable active content, which triggers the malicious PowerShell script. The hidden malware will be executed when the user downloads the malicious excel sheet or the image.
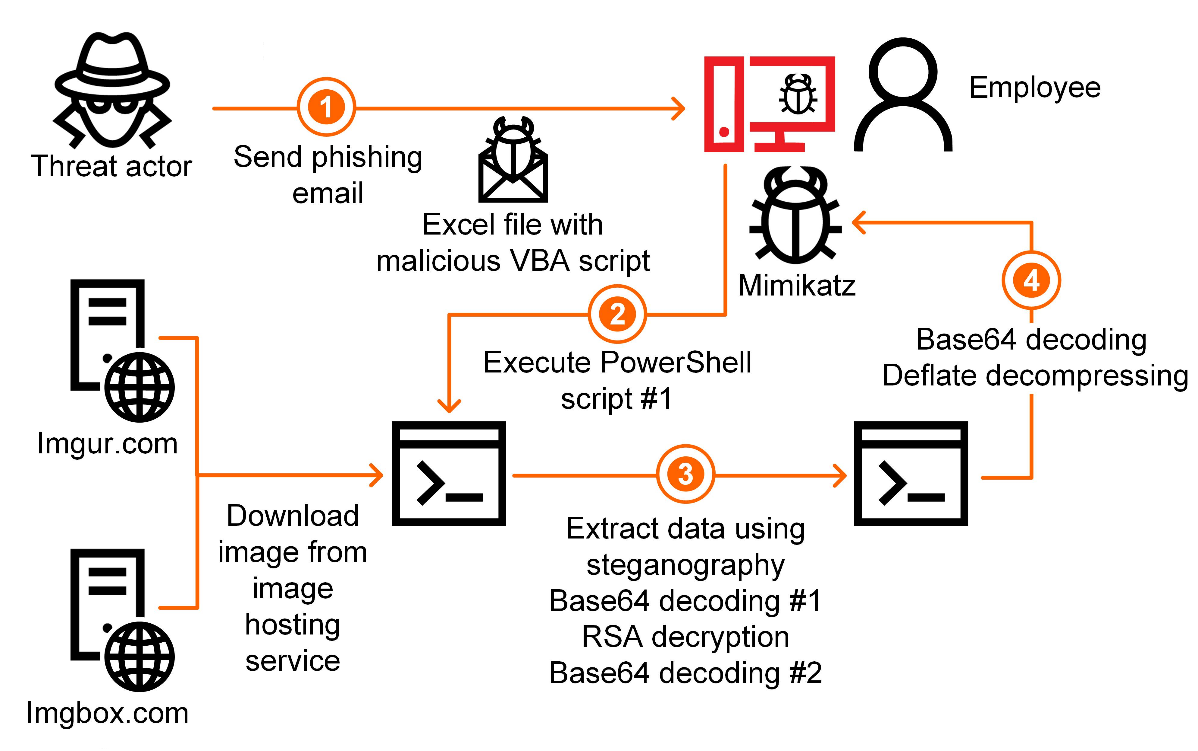
“The data is hidden in the image using steganographic techniques and is extracted by the malware from pixels defined by the algorithm. Using steganography enables the attackers to evade some security tools, including network traffic scanners. The data extracted from the image is consecutively encoded using the Base64 algorithm, encrypted with the RSA algorithm and encoded using Base64 again,” researchers added.
Preventive Measures
Kaspersky has also listed certain preventive measures to mitigate these kinds of attacks, these include:
- Train employees at enterprises in using email securely and, specifically, in identifying phishing messages
- Restrict macros in Microsoft Office documents
- Restrict PowerShell script execution
- Pay special attention to events of launching PowerShell processes initiated by Microsoft Office applications
- Restrict the ability of programs to gain SeDebugPrivilege privileges
- Install antivirus software with support for centrally managing the security policy on all systems; keep the antivirus databases and program modules of security solutions up to date
- Use accounts with domain administrator privileges only when necessary. After using such accounts, restart the system on which the authentication was performed
- Implement a password policy with password strength and regular password change requirements
- If it is suspected that some systems are infected, scan these systems with antivirus software and force a change of passwords for all accounts that have been used to log on to compromised systems






















