
Despite several employee awareness programs and cybersecurity best practices, most organizations face insider threats that affect the overall security posture. Threat actors continue to target unwitting employees – the weakest link – with different social engineering and phishing lures hitting the mailboxes.
According to Egress’ Insider Data Breach Survey 2021, 94% of organizations sustained insider data breaches last year. Nearly 84% of security leaders surveyed stated that human error was the top cause of cyberattacks, while 28% of the respondents admitted that insiders’ malicious intent is their biggest fear.
By Rudra Srinivas, Senior Feature Writer, CISO MAG
Insider Threats on Rise
Insider threats and attacks become a burning issue for organizations globally, as a single negligent act of an employee could cost a fortune for the company’s security. Insider threats increased by 47%, from 3,200 in 2018 to 4,716 in 2020. The cost of insider threat incidents also surged by 31%, from $8.76 million in 2018 to $11.45 million in 2020. Employee negligence led to 62% of security incidents, costing global organizations an average of $307,111 per incident.
Types of Insiders
All insider attacks are not due to employee errors. Some attacks are the result of employees with malicious intent.
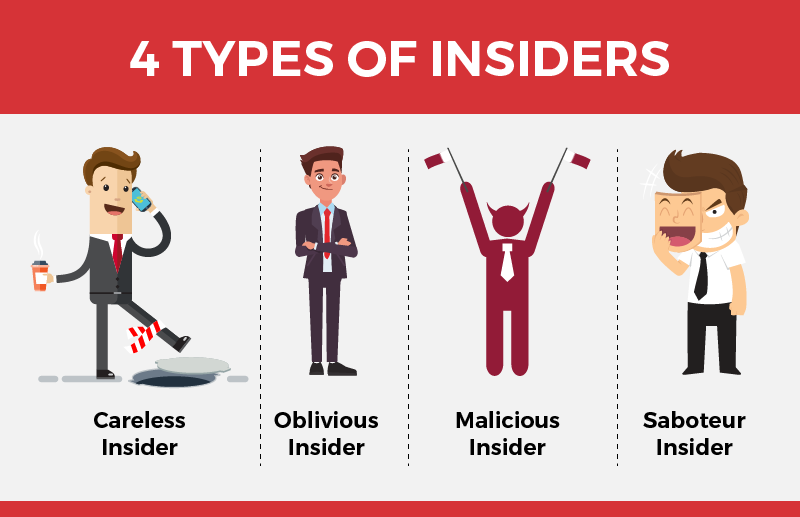
1. Careless Insider
The careless/negligent insiders are the common type of insiders that most organizations face. These insiders have no ill intentions towards the company; however, their negligent acts create chaos. The common actions (harmful yet unintentional) of a careless insider includes clicking/downloading malicious attachments, responding to phishing lures, and leaving flash drives containing sensitive data unattended, etc.
2. Oblivious Insider
Oblivious insiders have access to the company’s confidential data, making them a primary target for phishers. Attackers often trick these insiders via social engineering to obtain sensitive data or deploy malware.
3. Malicious Insider
These insiders purposefully cause damage to the organization’s security by erasing/stealing sensitive corporate data or helping outsiders deploy malware or ransomware.
4. Saboteur Insider
Insiders making career shifts come under this category. Saboteurs intentionally try to harm their current company’s reputation to show their frustration. Saboteur insiders take revenge against their present company by giving hackers corporate data and vulnerability exploits.
Best Practices
While we cannot predict insider actions, implementing certain security actions could mitigate the risks. These include:
- Providing cybersecurity education and training to all employees to boost endpoint security
- Encouraging all employees and third-party users to maintain cyber by choosing complex passwords (Eg.: “T1g3rudhxn!vo?LSU”)
- Establishing physical security in work environments by inspecting everyone entering critical IT server rooms
- Monitoring remote access from all endpoints and mobile devices
- Creating a backup system or backup policy
Note: Do not use the passwords used as example in this article for your actual password.
About the Author
Rudra Srinivas is a Senior Feature Writer and part of the editorial team at CISO MAG. He writes news and feature stories on cybersecurity trends.
More from the Rudra.
















