
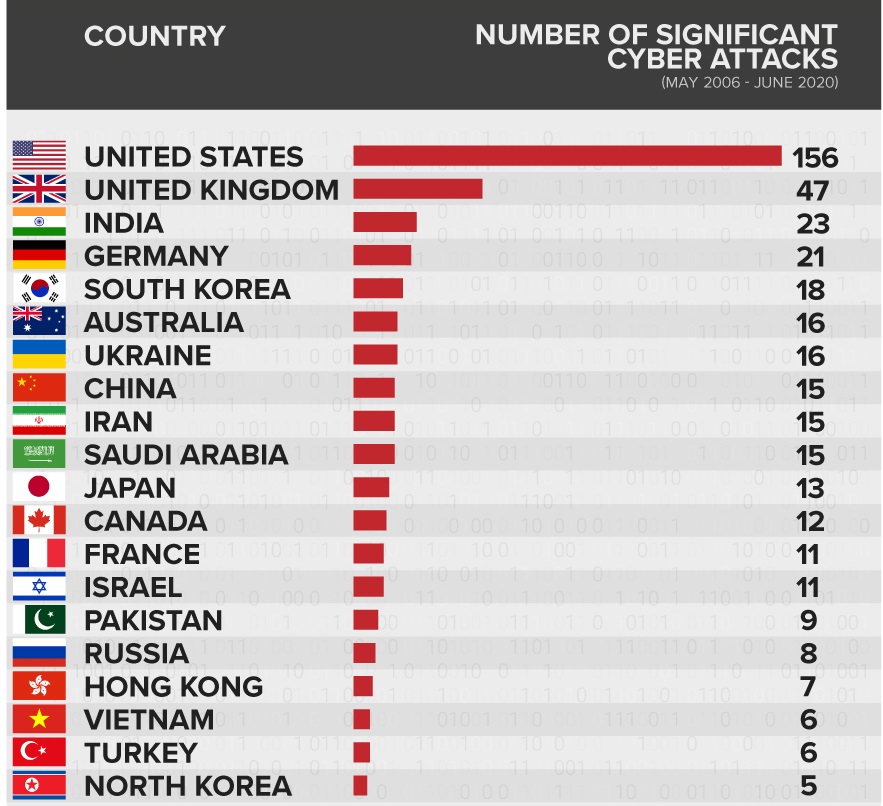
A report from Specops Software stated that the U.S., the U.K., India, and Germany have suffered significant cyberattacks over the past 14 years. Specops defined “significant cyberattacks” as attacks targeted at a country’s government agencies, defense units, high-tech organizations — or economic crimes with losses more than a million dollars.
The report, which analyzed data from the Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS), found that the U.S. has experienced the most significant cyberattacks, totaling 156 attacks reported between May 2006 and June 2020. The U.K. ranked second-highest, with 47 significant attacks reported during the same period. India ranked third, with 23 large scale attacks followed by Germany with 21 attacks. Next on the list was South Korea (18 attacks), Australia and Ukraine (both 16 attacks). Whereas, the countries least exposed to cyberattacks were Vietnam, Turkey, and North Korea.
According to the research, the majority of the attack techniques used by cybercriminals to launch significant cyberattacks were: Distributed Denial of Service Attack (DDoS), SQL Injection attack, man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks, and phishing attacks.
Most Vulnerable Countries
A similar survey, “Cybersecurity Exposure Index (CEI) 2020,” by password security resource PasswordManagers.co analyzed and ranked 108 countries based on their exposure to Trojans, malware, and phishing attacks. It also revealed the level of cybersecurity commitment across Europe, America, Asia-Pacific, and Africa.
According to the survey report, Finland is the least exposed country to cybercrimes, followed by Denmark, Luxembourg, Australia, and Estonia. Afghanistan topped the list as the most exposed country to cyberattacks, followed by Myanmar, Ethiopia, Palestine, and Venezuela. The survey measured the cybersecurity exposure score of each country from 0-1 (low-high exposure). It is found that Europe has the lowest exposure score (0.329), followed by North America (0.462). Nearly, 70.73% of European countries are classified in the low and very low exposure groups.










