
Researchers at Promon, a cybersecurity firm better known for its in-app security protection, had earlier discovered a vulnerability in the Android operating system named “StrandHogg”. This vulnerability enabled cybercriminals to hijack legitimate apps and perform malicious operations. But having learned from its shortfalls, the StrandHogg 2.0 vulnerability now enables cybercriminals to hijack nearly any app running on Android 9.0 devices and below.
StrandHogg 2.0 Vulnerability
The Promon researchers found a new elevation of privilege vulnerability classified as “critical severity” (CVE-2020-0096) by Google. One of the reasons for its severity being termed as “critical” is because it allows cybercriminals to gain access to almost all apps. The earlier version of StrandHogg exploited the Android control setting ‘TaskAffinity’, which hijacked Android’s multitasking feature and, as a result, left behind traceable markers. However, this was worked around in StrandHogg 2.0 as it does not exploit the Android control setting ‘TaskAffinity’ and thus difficult to detect.
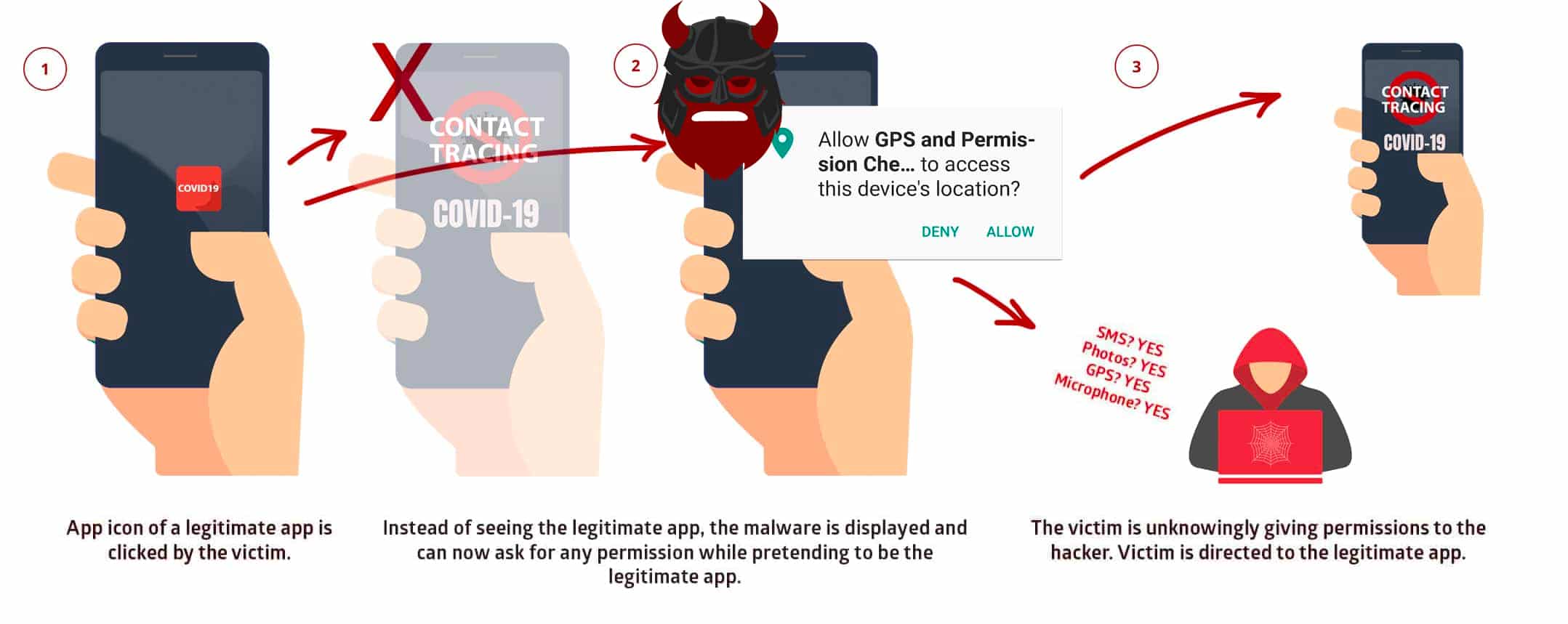
The StrandHogg 2.0 vulnerability allows potential cybercriminals to take app controls and:
- Listen and record user and phone call conversations through the microphone
- Unknowingly take camera controls and click photos
- Read and send SMSs
- Exfiltrate users’ login credentials used in different mobile apps and accounts
- Access and exfiltrate data files and photos from the device
- Track device location and gain GPS information
- Access the contacts list on the device
- Access phone logs
StrandHogg 2.0 vulnerability is a severe threat as it could be exploited without gaining root access, however, it has not yet been exploited in the wild. Meanwhile, Android has already rolled out security patches for its Android ecosystem partners in April 2020 and was expected to apply the same to the current Android versions 8.0, 8.1, and 9.0 soon after.










