
While the world is reeling from the aftereffects of the pandemic, cyberspace is getting infected with the first ransomware strain of 2021. Dubbed as Babuk Locker, the new ransomware appears to have allegedly compromised the corporate networks of some companies globally. According to security researcher Chuong Dong, Babuk Locker ransomware is encrypting victims’ sensitive information and demanding a ransom of $60,000 to $85,000 in Bitcoins.
Babuk Locker Traits
Chuong Dong claimed that Babuk Locker uses new techniques like multi-threading encryption and abuses the Windows Restart Manager. The ransomware implements SHA256 hashing, ChaCha8 encryption, and Elliptic-curve Diffie–Hellman (ECDH) key generation for encrypting scheme. It also can spread its encryption via available networks and uses an exchange algorithm to safeguard its keys and encrypt files from detection.
“Similar to Conti or REvil ransomware, Babuk utilizes the Windows Restart Manager to terminate any process that is using files. This ensures that nothing prevents it from opening and encrypting the files. This is accomplished through the calls RmStartSession, RmRegisterResources, and RmGetList to get a list of processes that are using a specified file. If the process is not explorer.exe or a critical process, then Babuk will call TerminateProcess to kill it,” Dong said.
How Babuk Locker Encryption Works?
For encryption, Babuk Locker ransomware uses two ChaCha8 keys generated from the ECDH shared secret’s SHA256 hash and the first 12 bytes of the shared secret as encryption keys.
Babuk’s file encryption is of two different types — Small File Encryption and Large File Encryption. Small files (around 41 MB) are mapped entirely and encrypted with ChaCha8 two times. Whereas, the encryption process is different in large files. They are divided into three equally large regions, and for each of these regions, only the first 10 MB is encrypted.
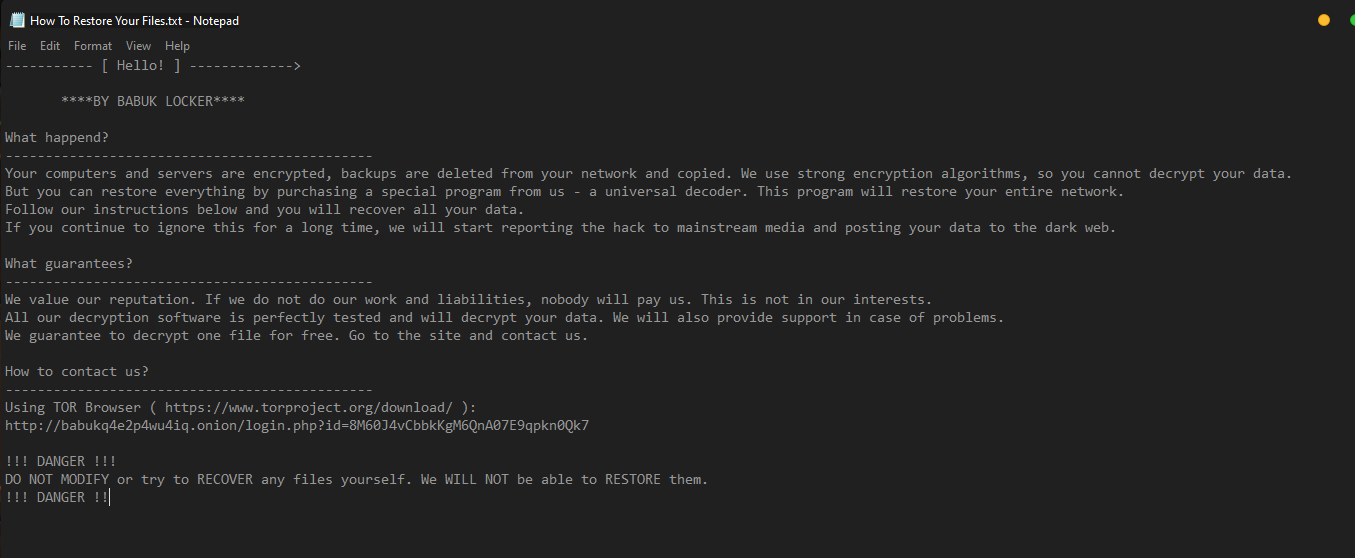
Ransom Note
Other Findings
- Despite the amateur coding practices used, Babuk’s strong encryption scheme utilizes the Elliptic-curve Diffie–Hellman algorithm, which has proven effective in attacking a lot of companies so far.
- Because the malware authors are using one private key for each Babuk sample, it’s clear that their main target is large corporations instead of normal computer users.
- As per the website embedded in the ransom note and the leaks on Raidforums, they have successfully compromised five different companies in the world.
Indicators of Compromise
MD5: e10713a4a5f635767dcd54d609bed977
SHA256: 8203c2f00ecd3ae960cb3247a7d7bfb35e55c38939607c85dbdb5c92f0495fa9
Babuk ransomware comes in the form of a 32-bit .exe file.





















