
India celebrated its 74th Independence Day on August 15, 2020. On this occasion, the Hon. Prime Minister of India, Narendra Modi, in his address to the nation said, “Threats from cyberspace can endanger all aspects of Indian life, and the government is alert on this.” Thus, to protect the data sovereignty and privacy of all its citizens, PM Modi announced that India was soon going to introduce a new cybersecurity policy. The “soon” seems to have come “sooner” this time as the National Health Authority (NHA) of India has now released the first draft of the health data management policy for the National Digital Health Mission (NDHM).
What is the National Digital Health Mission (NDHM)
National Health Stack (NHS) was formulated in 2018 by the Government of India (GoI), whose sole motive was to provide foundational components required for the health IT programs in India under the able stewardship of J. Satyanarayana, former Secretary of MeitY and UIDAI. This committee studied the current health infrastructure in India, the need and integration of IT, and the most important part – the laws and governance of the eHealth infrastructure. Post its findings, a report was submitted to the GoI called the National Digital Health Blueprint (NDHB), which is now being placed in the public domain for open discussion. Based on this report, the government has formulated a framework to integrate digital technology in the health care sector under the name National Digital Health Mission (NDHM).
Key Features of National Digital Health Blueprint
The key features of the blueprint provided by the NDHM include:
- A federated architecture
- Set of architectural principles
- 5-layered system of architectural building blocks
- Unique Health ID (UHID)
- Privacy and consent management
- National portability
- EHR (Electronic Health Records)
- Applicable standards and regulations
- Health analytics
- Multiple access channels like call center, Digital Health India portal and MyHealth App.
NDHBs Building Blocks
The NDHB identified 23 building blocks in total, however, based on the existing health systems and discussions with other stakeholders, the following 5+2 layered architecture building blocks have been identified as the most critical.
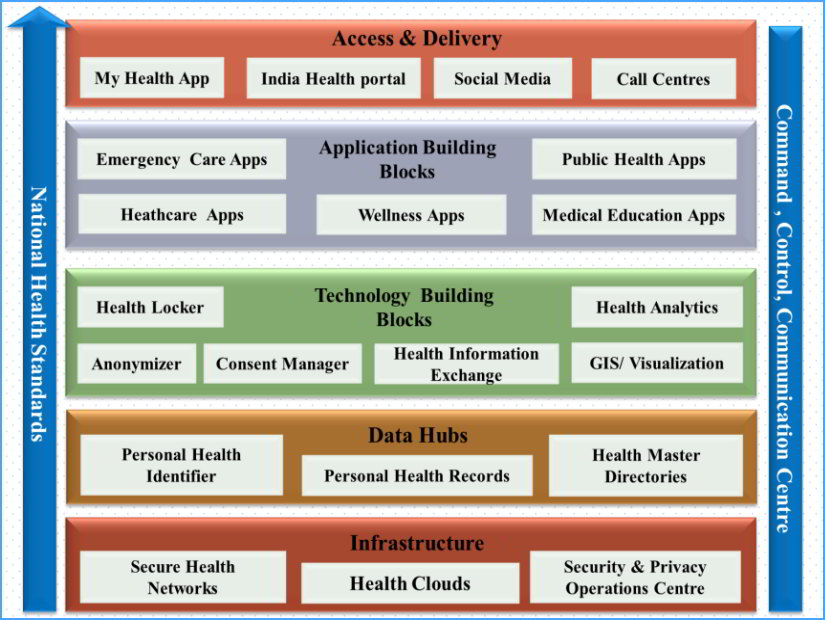
As seen in the above image, the National Digital Health Mission has made security and privacy of health data and its associated networks the basis of this framework (refer to Infrastructure Layer/Layer 1 in the image). This pretty much sums up the Government of India’s strict stand on digital security and the fact that it is looking forward to building a strong framework on the sturdy foundation of data security and privacy. According to the draft, any “sensitive personal information” can be collected only in accordance with the policy and consent of all stakeholders.
Talking to the media, Dr. Indu Bhushan, CEO of NHA, said, “The Draft Health Data Management Policy is the maiden step in realizing NDHM’s guiding principle of “Security and Privacy by Design” for the protection of individual’s data privacy. It encompasses various aspects pertaining to health care data such as data privacy, consent management, data sharing, and protection, etc.”
For further discussions on the draft, the government has sought comments from the public latest by September 03, 2020.










