
Strong login credentials are treated as the first defense against unauthorized intrusions. However, they also become a gateway for cybercriminals to penetrate critical network systems. Threat actors mostly obtain sensitive login information like usernames, passwords, or passcodes via data breaches and underground dark web forums. They often abuse stolen credentials to launch various cybercriminal activities, such as compromising a network or deploying ransomware.
By Rudra Srinivas, Senior Feature Writer, CISO MAG
What is a Credential Abuse Attack?
In credential abuse attacks, scammers leverage illicitly obtained credentials to break into user accounts by adding a list of compromised usernames and passwords to botnets. These botnets are designed to initiate the authentication process on targeted victim accounts. Once attackers get hold of a system or employee account, they move freely across the organization’s network by bypassing all security scans. Attackers further try to steal classified corporate data or exploit other accounts by leveraging one compromised account. They could also launch various attacks, including identity theft, phishing, impersonation scams, and other data abuse acts.
How Credential Abuse Attack Works
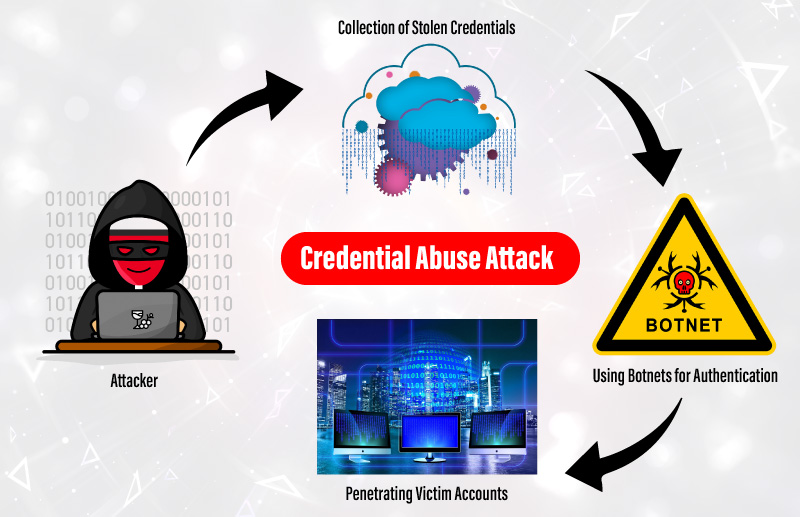
Credential abuse attacks are easy to execute and have a higher success rate because most users reuse passwords for multiple accounts.
Also Read: What is an SQL Injection Attack and How to Prevent it?
How to Prevent Credential Abuse
Having strong credentials will not prevent data breaches and hacker intrusions. Continuous security measures can help prevent unauthorized users from accessing corporate accounts. Here are some actionable steps to protect online accounts against credential abuse attacks:
1. Multiple Authentication Process
Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) or multi-factor authentication (MFA) processes to avoid unauthorized intrusions. Organizations can also implement passwordless authentication processes like biometrics or behavioral patterns to verify the user’s authenticity.
2. Enable Secondary Password Procedure
Along with password, organizations can prompt users to provide additional security inputs like PIN, Passcodes, or a security question.
3. Enable CAPTCHA
Ask users to solve a CAPTCHA for each login trail to help prevent unauthorized or automated login attempts.
4. Identifying Leaked Passwords
Reusing passwords is one of the primary reasons for credential abuse attacks. Check whether your credentials or other personal data have been leaked in any data breach on the haveibeenpwned website. Avoid reusing leaked/breached credentials and update them regularly.
5. Responsible Disclosure
Notify users and employees about data leaks or unusual security events as they happen.
About the Author
Rudra Srinivas is a Senior Feature Writer and part of the editorial team at CISO MAG. He writes news and feature stories on cybersecurity trends.
More from the Rudra.











